What is DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy): Understanding Its Principles and Benefits
Dialectical Behavior Therapy, or DBT, is a type of talk therapy created to help people manage their emotions and improve their relationships. It teaches skills for dealing with stress, regulating emotions, and enhancing communication. Designed originally for those with borderline personality disorder, it has shown benefits for various mental health issues.
DBT combines individual therapy with group skills training. During sessions, individuals learn practical techniques that can be used in daily life. This approach creates a space for personal growth and self-discovery, making it easier for individuals to handle difficult situations.
Many find DBT helpful because it offers tools that promote change and acceptance. This therapy emphasizes balancing opposites, like acceptance and change, which can be powerful for someone struggling with intense feelings or challenges. Readers will discover how DBT works and who can benefit from it.
Foundations of DBT
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, is built on a strong foundation of history and key principles. These elements shape how DBT is practiced and understood today.
Historical Context
DBT was created in the late 1980s by Dr. Marsha Linehan. It was originally designed for people with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). Dr. Linehan noticed that traditional therapies often did not help these patients effectively.
She combined cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices. This blend allowed her to address emotional instability while teaching coping skills. Over the years, DBT has gained recognition and has been adapted for various conditions like depression and anxiety.
Core Theoretical Principles
DBT relies on several core principles that guide its approach. One essential element is the concept of dialectics. This idea focuses on the balance between acceptance and change. It teaches clients to accept their current situation while working towards improvement.
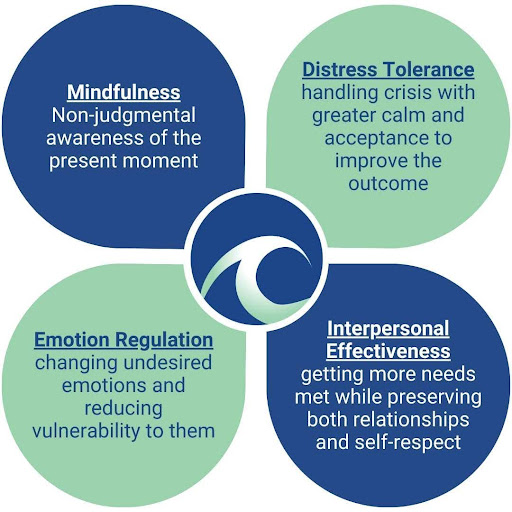
Another key principle is the emphasis on skills training. Clients learn crucial skills in four main areas: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. These skills help individuals handle challenging situations more effectively.
Lastly, DBT highlights the importance of the therapeutic relationship. A strong connection between the therapist and the client can lead to better outcomes. The therapist provides support while encouraging growth and change.
DBT Components
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) consists of essential components that help individuals learn skills to manage emotions, improve relationships, and reduce distress. Key elements include the stages of treatment and the standard modules used in therapy sessions.
Stages of Treatment
DBT follows a structured approach with four main stages.
- Stage One focuses on stabilizing the individual. It emphasizes reducing harmful behaviors, such as self-harm and suicidality. Clients work to achieve safety and learn skills for emotion regulation.
- Stage Two aims at treating emotional suffering from past trauma. In this stage, individuals learn to process their feelings and experiences better. They practice skills to manage trauma-related emotions.
- Stage Three helps clients build self-esteem. This stage involves improving self-image and developing personal goals. Clients learn to find fulfillment in life.
- Stage Four focuses on enhancing the quality of life. Individuals work on building a life that is meaningful and satisfying. Advanced skills are practiced to maintain emotional balance.
Standard Modules
DBT includes specific modules that teach important skills. These modules are designed to help individuals cope with stress and improve their relationships.
- Mindfulness helps people stay present and focused. Skills learned in this module teach individuals how to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Emotion Regulation provides techniques to manage intense feelings. This module enables individuals to recognize their emotions and respond to them in healthy ways.
- Distress Tolerance equips individuals with strategies to handle crises. Skills learned here enable people to endure difficult moments without resorting to unhealthy behaviors.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness focuses on communication skills. It teaches individuals how to assert their needs while respecting others.
These modules work together to support a comprehensive approach to treatment in DBT.
Implementation in Therapy
DBT uses specific methods to help individuals improve their emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness. This section will explore the key components such as therapeutic techniques, skills training groups, individual therapy, and phone coaching.
Therapeutic Techniques
Therapeutic techniques in DBT focus on building a strong therapeutic alliance. The therapist and client work closely together to identify problems and set goals.
Key techniques include mindfulness, where individuals learn to stay present and aware, and validation, which helps clients feel understood.
These techniques encourage clients to accept their feelings while also working on change. By using these methods, therapists guide clients through stress and help them cope with difficult emotions.
Skills Training Groups
Skills training groups are a vital part of DBT. In these groups, clients learn and practice specific skills that help them manage their emotions.
The skills are divided into four main areas:
- Mindfulness: Focusing on the present moment.
- Distress Tolerance: Creating ways to cope with pain without making things worse.
- Emotion Regulation: Understanding and managing emotions effectively.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: Improving communication and relationships.
Groups offer a supportive environment where clients can share experiences and practice skills with peers.
Individual Therapy
Individual therapy provides a space for personalized support. During these sessions, the therapist tailors the approach to meet the specific needs of the client.
Clients work on applying skills from group sessions to real-life situations. This helps in recognizing triggers and developing coping strategies.
Therapists also keep track of progress and adjust goals when necessary. This one-on-one time is crucial for deeper work on emotional issues.
Phone Coaching
Phone coaching is a unique feature of DBT that supports clients between therapy sessions. When clients face challenges, they can reach out to their therapist for guidance.
This service allows clients to apply skills in real-time, which reinforces learning. Clients can discuss specific situations and work on immediate coping strategies.
Phone coaching helps maintain the focus on behavior change and accountability, making it a useful tool in DBT.
Research and Efficacy
Many studies show that DBT is effective in treating various mental health disorders. It focuses on improving emotional regulation, interpersonal skills, and coping strategies.
Clinical Trials and Outcomes
Clinical trials have examined DBT’s effectiveness in various settings. Research indicates that patients often experience reduced symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD). Many studies report a decrease in self-harm behaviors and hospitalizations.
For instance, one study found that 77% of participants showed improvement after completing DBT. Another study highlighted a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms in individuals also diagnosed with BPD. These findings support its use in clinical settings, with results reflecting positive long-term benefits.
Applications and Limitations
DBT is widely used for treating BPD but can also benefit those with depression, anxiety, and eating disorders. Many therapists apply it to help patients manage intense emotions and build better relationships.
Despite its strengths, DBT may not work for everyone. Some individuals might struggle with the commitment required in skill-building. It also requires trained professionals to lead therapy sessions effectively. Understanding these aspects helps in setting realistic expectations for treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries about Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT). It covers how DBT operates, the techniques used, comparisons with other therapies, and conditions treated, along with tips on finding a therapist.
How does Dialectical Behavior Therapy work and what are its goals?
DBT helps people learn skills to manage emotions and improve relationships. It blends individual therapy with group skill-building sessions. The main goals include reducing self-destructive behaviors and increasing emotional regulation.
Is DBT useful in treating alcohol and drug addiction?
Yes, DBT can be very useful for treating alcohol and drug addiction. It helps people manage urges, cope with stress, and handle difficult emotions without turning to substances. DBT also focuses on building a balanced life and creating healthy relationships, which are essential in recovery.
What does DBT entail?
DBT includes four main areas of skill-building: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. In therapy, people learn practical tools to handle strong emotions, communicate better, and reduce harmful behaviors. DBT can be done in individual therapy sessions, group skills training, or both.
What are “How” skills in DBT?
The “How” skills in DBT teach people how to practice mindfulness effectively. They are:
- Non-judgmentally: Observing thoughts and feelings without judging them as “good” or “bad”.
- One-mindfully: Focusing on one thing at a time to stay present.
- Effectively: Doing what works best in a given situation, rather than reacting out of habit.
Is DBT therapy only for personality disorders?
No, DBT isn’t just for personality disorders! While it was originally designed for people with borderline personality disorder, it is now used to help with a range of mental health issues. People with depression, anxiety, PTSD, eating disorders, and substance use disorders also benefit from DBT.
What is a dialectic in DBT?
In Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), a dialectic refers to the concept of holding two seemingly opposing ideas or truths at the same time. The goal of a dialectic is to find a balance between these opposites, creating a “middle path” rather than viewing things as all-or-nothing. This approach encourages flexibility in thinking and helps people move away from more black-and-white views.
For instance, a common dialectic in DBT is the balance between acceptance and change. DBT teaches that individuals must accept themselves and their circumstances as they are, while also working towards positive change.
Can you provide examples of DBT techniques and how they’re applied in therapy?
DBT uses several practical techniques. Mindfulness helps individuals become aware of their thoughts and feelings without judgment. Distress tolerance skills teach coping strategies during tough times. Interpersonal effectiveness helps improve communication and relationships.
What distinguishes Dialectical Behavior Therapy from Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
DBT focuses on balance, combining acceptance and change. While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) mainly targets changing negative thoughts, DBT emphasizes understanding emotions. DBT also includes a strong support system through group therapy. For more, check out our post dedicated to Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of undergoing DBT?
Benefits of DBT include improved emotion regulation and decreased self-harm. It also enhances interpersonal skills. A drawback may be the time commitment needed for sessions and homework, which can be challenging for some individuals.
What are the six main points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy?
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) incorporates six main points or components to foster emotional regulation, self-awareness and improve behavior. Here is an outline of the six main points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy:
- Mindfulness: This skill focuses on being present in the moment, increasing self-awareness, and reducing impulsive reactions.
- Distress Tolerance: This component teaches skills to cope with intense, immediate distress in healthier ways. Rather than trying to change or escape distressing situations, individuals learn to tolerate and accept difficult emotions.
- Emotion Regulation: Emotion regulation skills help people understand and manage their emotions. This reduces vulnerability to intense mood swings and promotes healthier emotional responses to challenging situations.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: These skills focus on improving communication and building stronger, more positive relationships. Individuals learn strategies to assert their needs, set boundaries, and navigate conflicts in a healthy way.
- Walking the Middle Path: This component encourages balance and compromise, helping individuals avoid extreme “all-or-nothing” thinking. By finding a middle ground, they can make more balanced and thoughtful decisions.
- Acceptance and Change: DBT emphasizes the importance of both accepting oneself and working towards meaningful change. This dialectical approach fosters self-compassion while motivating individuals to grow and make positive adjustments in their lives.
Each of these points works together to help people build resilience, improve coping mechanisms, and ultimately lead more fulfilling lives.
What types of disorders or conditions are typically treated with DBT?
DBT is often used for borderline personality disorder, but it can also help with depression, anxiety, and PTSD. It is suitable for those who struggle with intense emotions and unstable relationships.
How can someone find DBT therapy sessions, and what should they expect?
To find DBT therapy, individuals can search online directories or ask their doctors. In therapy, they can expect a mix of counseling and skill-building classes. Sessions usually involve discussing challenges and applying DBT techniques. The most simple way to get started is to reach out to a professional. Our care team is standing by and ready to help. Call (774) 619-7750 today for a free consultation.