EMDR vs DBT: Understanding the Differences in Therapeutic Approaches
EMDR vs DBT: Which one works the best? Both Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are effective therapeutic approaches. Each has unique methods and focuses, making them suited for different situations. Choosing between EMDR and DBT depends largely on the specific mental health needs and goals of the individual.
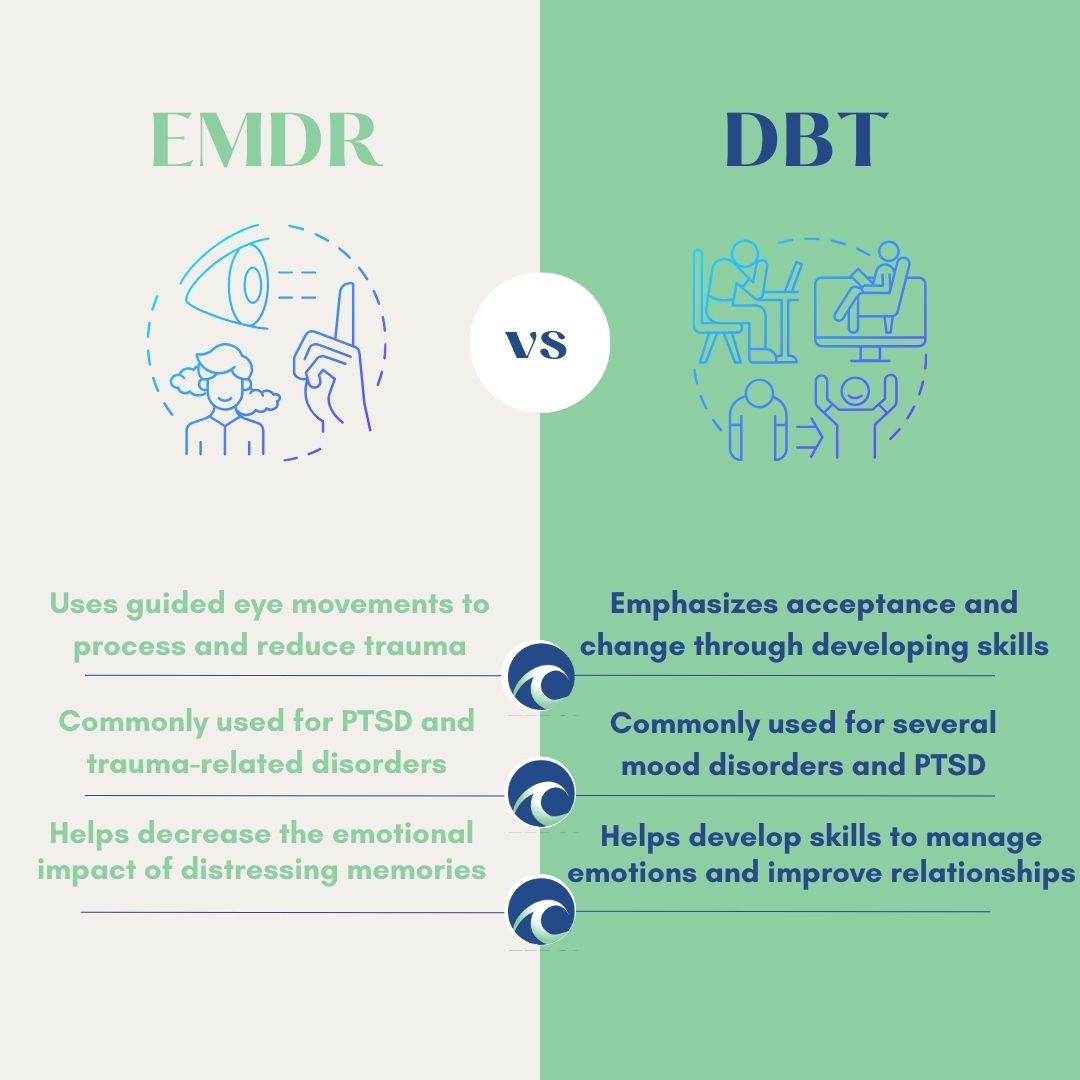
EMDR is often used for trauma and PTSD. It helps individuals process distressing memories through guided eye movements. In contrast, DBT focuses on emotions and relationships, particularly for those with borderline personality disorder. It teaches skills to manage intense emotions and improve relationships.
Understanding which therapy is right for someone requires looking at their personal experiences and therapy goals. The differences between these two therapies can significantly impact a person’s healing journey.
Overview of EMDR
EMDR, or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing, is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals process traumatic memories. It combines elements of psychotherapy with bilateral stimulation, which can include side-to-side eye movements. This approach has a specific history and core principles that shape its effectiveness.
History and Development
EMDR was developed in the late 1980s by Francine Shapiro. She observed that certain eye movements seemed to reduce the intensity of distressing thoughts. The method quickly gained attention for its potential in treating trauma.
In 1989, Shapiro published the first study on EMDR, which showed promising results for those with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Over the years, the method evolved through research and clinical practice, leading to its recognition as an effective treatment. Today, EMDR is widely accepted and practiced by therapists worldwide.
Core Principles of EMDR
The core principles of EMDR focus on processing distressing memories. The therapy works on the idea that traumatic memories can become stuck in the brain, causing ongoing emotional pain.
During sessions, clients recall traumatic events while engaging in bilateral stimulation, such as following hand movements. This process helps reprocess the memories, allowing individuals to integrate them into their experiences.
Key components of EMDR include:
- Dual Attention: Fostering focus on both the memory and the present moment.
- Desensitization: Reducing the emotional charge of the traumatic memory.
- Installation: Promoting positive beliefs related to trauma.
These principles guide the therapeutic process, making EMDR a unique option for those seeking relief from trauma.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) Explained
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of therapy that helps people manage emotions and improve relationships. It was designed for those who struggle with intense feelings and behaviors, particularly in borderline personality disorder.
Click here to watch a short video explaining “What is DBT”.
Foundations of DBT
DBT was created by psychologist Marsha Linehan in the 1980s. It combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices.
The word “dialectical” means balancing two opposites. In this case, it refers to accepting one’s feelings while also working to change harmful behaviors. This balance is essential for people who experience extreme emotions.
DBT emphasizes the importance of being present in the moment and understanding one’s thoughts and feelings. This approach helps individuals learn to navigate their emotional experiences more effectively.
Main Components of DBT
DBT consists of four main components:
- Mindfulness: This practice teaches individuals to focus on the present. It helps them become aware of their thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Distress Tolerance: This skill helps people cope with painful emotions. It teaches strategies to handle crises without resorting to harmful actions.
- Emotion Regulation: This component focuses on recognizing and changing emotional responses. Individuals learn how to manage emotional reactions in healthy ways.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: This skill helps improve communication. It teaches people how to express their needs and set boundaries in relationships.
Together, these components guide individuals to live more balanced and fulfilling lives. Each element builds on the others, providing a comprehensive approach to emotional health.
Comparative Analysis: EMDR vs DBT
EMDR vs DBT. EMDR and DBT are both valuable therapeutic approaches, each designed for specific issues. Their methods and results vary significantly, which can influence their effectiveness depending on the individual’s needs.
Differences in Treatment Approaches. EMDR vs DBT
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) focuses on processing traumatic memories. It uses bilateral stimulation, such as eye movements, to help clients reprocess distressing thoughts. This method aims to reduce the emotional intensity of the memories.
DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy), on the other hand, integrates cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness. It helps individuals manage emotions and improve relationships. DBT emphasizes balancing acceptance and change, teaching skills for emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness.
Effectiveness for Different Conditions
EMDR is particularly effective for PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), anxiety, and trauma-related disorders. Research shows significant reductions in symptoms after EMDR sessions.
DBT is beneficial for individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD), self-harming behaviors, and suicidal thoughts. Its structure helps clients build coping skills and reduce emotional distress.
Therapeutic Techniques and Outcomes
EMDR involves a structured eight-phase approach. It includes client history assessment, memory processing, and installation of positive beliefs. Outcomes often include reduced trauma symptoms and improved emotional well-being.
DBT includes skills training in areas like mindfulness, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. It also involves individual therapy sessions and group skills training. These techniques lead to improved emotional regulation and better relationships.
Considerations for Therapy Selection
Choosing between EMDR and DBT requires careful thought. Each therapy has specific uses that align with different patient needs. It’s essential to assess the individual situation and recognize potential challenges in therapy selection.
Assessment of Patient Needs
Understanding a patient’s specific needs is critical in therapy selection. EMDR is effective for trauma, helping individuals process distressing memories. It may suit someone with PTSD or strong anxiety related to past events.
DBT focuses on emotional regulation and interpersonal skills. It is beneficial for individuals with borderline personality disorder or those facing intense mood swings.
To make the right choice, therapists should consider:
- Patient history: Past trauma or emotional issues.
- Current symptoms: The severity and type of distress.
- Treatment goals: What the patient hopes to achieve.
A thorough assessment can help guide the decision for the best therapy method.
Limitations and Challenges
Each therapy has limitations and challenges that can affect treatment outcomes. EMDR requires a trained therapist. Not all regions have access to professionals skilled in this method.
Some patients may also struggle with the intensity of EMDR sessions. This can lead to discomfort or avoidance, making progress difficult.
In contrast, DBT can be time-consuming. It often involves multiple sessions and skills training.
Furthermore, some patients may find group therapy settings daunting.
Awareness of these factors helps in setting realistic expectations for therapy outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common questions about EMDR and DBT therapies, focusing on their differences, effectiveness, and specific use cases. It also explores how these therapies can be integrated and discusses alternatives.
What distinguishes EMDR from DBT in therapeutic approaches?
EMDR, or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing, mainly targets trauma and distressing memories. It uses specific techniques to process these memories and reduce their emotional impact.
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, focuses on emotional regulation and interpersonal skills. It is designed for people with intense emotions or behaviors, especially those with borderline personality disorder.
What are the comparative effectiveness of EMDR and DBT treatments?
EMDR is considered effective for treating PTSD and trauma-related conditions. Research shows it can lead to rapid improvement in symptoms.
DBT is effective for managing emotional regulation and reducing self-destructive behaviors. It often helps those with mood disorders and personality issues. Additionally, it has been shown to be effective in treating addiction.
Can EMDR and DBT therapies be integrated, and if so, how?
Integrating EMDR and DBT can be beneficial for patients with complex needs. Therapists may use DBT skills to help clients cope with emotions during EMDR sessions.
This combination can enhance emotional support while addressing trauma. The integration aims for a more comprehensive treatment approach.
For which patient conditions is DBT typically recommended?
DBT is recommended for individuals with borderline personality disorder. It is also useful for those experiencing severe depression, anxiety, and self-harm behaviors.
This therapy can benefit individuals struggling with intense emotions and unstable relationships. It focuses on improving coping skills and emotional management.
How does somatic therapy differ from EMDR, and when is each approach used?
Somatic therapy emphasizes physical awareness to process trauma. It focuses on how emotions manifest in the body and involves movement and breathwork.
EMDR targets memories using specific protocols. It is more structured and fast-paced, making it suitable for individuals with trauma-centric issues.
What are some alternatives to EMDR for trauma-informed therapy?
Alternatives to EMDR include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and art therapy. CBT focuses on changing negative thoughts related to trauma.
Art therapy offers a creative outlet for expressing emotions, helping clients process experiences without needing to talk about them directly.
EMDR and DBT at Waterside Behavioral Health
At Waterside Behavioral Health, both EMDR and DBT are offered as specialized treatment options tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. Our skilled clinicians utilize these therapies – sometimes together – to help patients effectively process trauma, regulate emotions, and build healthier coping skills for long-term mental wellness.
Getting Started with EMDR or DBT Therapy at Waterside Behavioral Health
Right now, you do not need to know which method of therapy is going to be best for you. Our programs offer you the ability to have an individualized treatment plan created with your clinician. You could try EMDR, DBT or any other of our offerings and build a plan around what works. Call us today at (774) 619-7750 if you or someone that you love might benefit from learning more about the path to wellness.




